Our Services
OUR SERVICES
- Broad Band
- Leased Line
- Wi-Fi and Hotspot
- Optical Fiber Networking
- Wired & Wireless Solutions
- CCTV Imaging
- Networking and Intranet
- Connectivity Solutions

The DSL (or Digital Subscriber Line) internet service makes its connection by utilizing unused telephone wires that cause no interruption to your telephone service. The speed you experience with a DSL connection varies with your distance from the switching station. Your speed will be slower the further away you are and faster the closer you are to the switching station and this may be a deciding factor when you attempt to select between a DSL line and a cable connection.
The newest broadband service is fiber-optic, which is the fastest Internet connection thus far. However, this type of Internet service is still in its infancy as its service areas are quite limited and because the laying down of the fiber-optic cable takes a while to complete. Wherever it is available, the cost not only competes with that of DSL and cable, but it provides a much faster connection than both of those services.
The broadband cable connection is provided by the local cable TV provider. Here the cable Internet connection speed varies with the number of users on the service at a specific point in time. Given a specific geographical area, users of the broadband cable service share the connection bandwidth which slows the speed the more users are on the system. This will occur at the peak times for example late in the evenings after the work day is over when many people will be accessing the Internet.
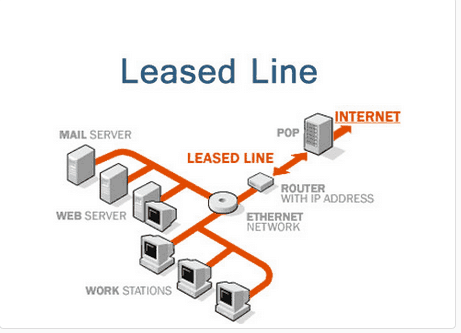
Leased lines were used to connect mainframe computers with terminals and remote sites, via IBM Systems Network Architecture (created in 1974) or DECnet (created in 1975).
With the extension of digital services in the 1980s, leased lines were used to connect customer premises to frame relay or ATM networks. Access data rates increased from the original T1 option up to T3 circuits.
Terminating a leased line with two routers can extend network capabilities across sites. Leased lines were first used in the 1970s by enterprise with proprietary protocols such as IBM System Network Architecture and Digital Equipment DECnet, and with TCP/IP in University and Research networks before the Internet became widely available. Note that other Layer 3 protocols were used such as Novell IPX on enterprise networks until TCP/IP became ubiquitous in the 2000s. Today, point to point data circuits are typically provisioned as either TDM, Ethernet, or Layer 3 MPLS.

WiFi hotspots are internet access points that allow you to connect to a WiFi network using your computer, smartphone or another device while away from your home or office network.
Many cities, businesses, and other organizations have begun offering WiFi hotspots, which help people stay connected to powerful, fast internet connections, which are often much faster than wireless cellular networks.
But what is a WiFi hotspot? How does it work? Are hotspots safe? Get all the information you need below.
A public WiFi hotspot works just like a Wi-Fi connection that you might find in your home or office. WiFi hotspots work by taking an internet connection and using special wireless equipment, such as modems and routers, to create a wireless connection, to which you can connect a tablet, smartphone, computer, or another device.
The range, power, speed, and price of a WiFi hotspot may vary, based on where you are. But the overall idea behind a WiFi hotspot is exactly the same as a home-based WiFi network, and you can connect to and use a WiFi hotspot just like you would use a home WiFi network.
Though WiFi hotspots are broadly similar, there are a few different types of hotspots available, and they do have some distinct differences. Let’s discuss these common types of WiFi hotspots now, and how they work.

A fiber optic cable consists of one or more strands of glass, each only slightly thicker than a human hair. The center of each strand is called the core, which provides the pathway for light to travel. The core is surrounded by a layer of glass called cladding that reflects light inward to avoid loss of signal and allow the light to pass through bends in the cable.
The two primary types of optical fiber cables are single mode and multi-mode. Single-mode fiber uses extremely thin glass strands and a laser to generate light, while multi-mode optical fiber cables use LEDs.
Single-mode optical fiber networks often use Wave Division Multiplexing techniques to increase the amount of data traffic that the strand can carry. WDM allows light at multiple different wavelengths to be combined (multiplexed) and later separated (de-multiplexed), effectively transmitting multiple communication streams through a single light pulse.
Fiber optic cables are moving toward supporting up to 10-Gbps signals. Typically, as the bandwidth capacity of a fiber optic cable increases, the more expensive it becomes.
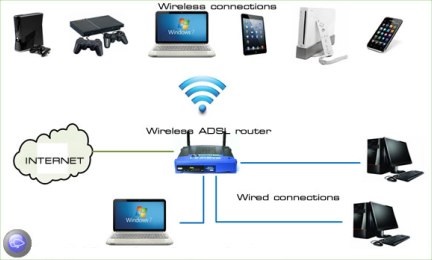
A wired network uses cables to connect devices, such as laptop or desktop computers, to the Internet or another network. A wired network has some disadvantages when compared to a wireless network. The biggest disadvantage is that your device is tethered to a router. The most common wired networks use cables connected at one end to an Ethernet port on the network router and at the other end to a computer or other device.
Previously it was thought that wired networks were faster and more secure than wireless networks. But continual enhancements to wireless network technology such as the Wi-Fi 6 networking standard have eroded speed and security differences between wired and wireless networks.
Many utility industry operators are looking for new ways to maximize their investment in communication networks while ensuring reliable, secure data transmission. There is a variety of communications solutions, the two most common being wireless technology and wired options-such as copper and fiber-optic cable.

When it comes to securing your business, there are many different types of CCTV to choose from. Surveillance plays a huge part in today’s society, and with cameras all around us, our day-to-day lives are experiencing higher levels of security each day.
What many people don’t know, however, is that there are a variety of different types of CCTV camera which suit different situations or premises, and that selecting the proper camera for the right application really is vital.
CCTV plays a huge part in today’s society, and with cameras all around us, our day-to-day lives are experiencing higher levels of security each day. What many people don’t know, however, is that there are a variety of different types of CCTV camera which suit different situations or premises, and that selecting the proper camera for the right application really is vital. Here, we run through these types of camera and what makes them unique and more suitable for some venues over others.
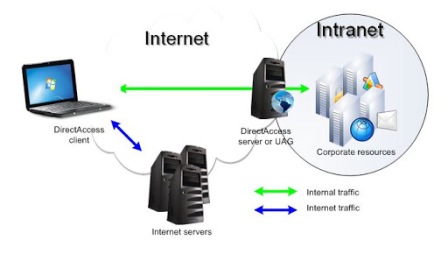
Sometimes the term refers only to the organization’s internal website, but may be a more extensive part of the organization’s information technology infrastructure. It may host multiple private websites and constitute an important component and focal point of internal communication and collaboration.
To put that another way, imagine all the computers owned by the company being connected to each other in exactly the same way as computers all over the world are connected to each other by the Internet. That would then be a company Intranet. There are other differences, obviously, of which the first is that this company Intranet, or network, does not necessarily have to be connected to the Internet proper. It could perfectly easily exist in total isolation from the rest of the world. There would also have to be extra software added to each computer so that the information stored on it would, in effect, be set up as the equivalent to a website complete with links to other web pages, but this could be easily done. The technology which creates web pages for the Internet can also create web pages for a company Intranet because the system is exactly the same. It even uses the same HTML coding and is designed to be accessed by the same Browsers.

Our Network Services deliver secure, reliable connectivity with low latency and high availability-whether you are connecting between geographically diverse locations or points within the data center.
It starts with your business. We understand that service interruptions are costly and disruptive to your bottom-line. Our network is built on the best industry carrier environments.
Get 100% core-network availability for secure converged data, voice and video traffic-all on a single network connection.
Support your global networking, security and business continuity requirements with Ethernet Virtual Private Line, Ethernet Private Line, Optical Wavelength Service and International Private Line.
Connect your users and bandwidth-intensive business applications, with superior peering and interconnectivity-plus reliability with a network recovery time of less than 50 milliseconds.
The challenge is to manage, secure and optimize end-to-end link traffic from headquarters all the way to remote locations ensuring the continuity of applications while controlling connectivity costs.
We are your single point of contact for all your network connectivity issues, taking ownership of problems to resolution. With End to End Networks, you have a partner who is dependable, accountable and always available.
Your personal – speed
& quality home connection Starting @ 599 / month

Why to Choose Us
Speeds at an Affordable Price
several other factors that should be taken into consideration besides just
the available download speeds.
7879888816
Email : adnpvt.ltd@gmail.com
